Breaking Down Barriers: Exercise for Disabilities and Wellness
Living with a disability poses unique challenges, but the power of exercise should never be underestimated. Physical activity not only enhances overall well-being but also plays a crucial role in improving the quality of life for individuals with disabilities. In this article, we will explore the importance of exercise for disabilities, discuss various types of adaptive exercises, and highlight the numerous benefits that regular physical activity can bring to those facing mobility challenges.

Understanding the Importance:
People with disabilities often face barriers that can limit their access to traditional forms of exercise. However, it's essential to recognize that everyone can benefit from physical activity, regardless of their abilities. Exercise for disabilities goes beyond the physical aspect; it encompasses mental and emotional well-being, social integration, and improved independence.
Adaptive Exercises for Different Disabilities:
Mobility Impairments:
Wheelchair Exercises:Tailored workouts focusing on upper body strength and flexibility, such as seated push-ups and resistance band exercises.
Water Aerobics: Buoyancy in water minimizes impact on joints, making it an ideal environment for individuals with mobility impairments to engage in cardiovascular activities.

Visual Impairments:
Guided Workouts: Utilizing audio cues or working with a fitness trainer experienced in adapting exercises for the visually impaired.
Tactile Feedback Equipment: Incorporating equipment with tactile feedback, such as textured mats or resistance bands with different textures.
Intellectual Disabilities:
Structured Routines: Providing clear and simple instructions, emphasizing routine and repetition.
Inclusive Group Activities: Encouraging participation in group exercises fosters a sense of community and support.
Neurological Conditions:
Adaptive Yoga: Modified yoga poses that focus on balance, flexibility, and relaxation can benefit individuals with conditions like multiple sclerosis or Parkinson's disease.
Aquatic Therapy: The buoyancy of water provides support and can enhance movement for individuals with neurological challenges.
Benefits of Exercise for Disabilities:
Improved Physical Health:
Enhanced cardiovascular health, muscle strength, and flexibility.
Better weight management and decreased risk of secondary health issues.
Mental and Emotional Well-being:
Stress reduction and improved mood through the release of endorphins.
Increased self-esteem and confidence through achieving fitness goals.
Social Integration:
Opportunities for socializing and building a supportive community.
Group exercises foster a sense of belonging and shared accomplishment.
Enhanced Independence:
Improved functional ability and daily living skills.
Greater autonomy and confidence in navigating daily tasks.
Conclusion:
Exercise for disabilities is a powerful tool that can positively impact the lives of individuals facing various challenges. It's essential to promote inclusivity in fitness spaces and provide adaptive exercise options that cater to diverse needs. By recognizing the importance of physical activity for everyone, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and empowering environment where individuals with disabilities can thrive and enjoy the numerous benefits of an active lifestyle.
 WEIGHT PLATES
WEIGHT PLATES
 Cast Iron Olympic Plates
Cast Iron Olympic Plates
 Olympic Rubber Weight Plates
Olympic Rubber Weight Plates
 PVC Weight Plates
PVC Weight Plates
 DUMBBELLS
DUMBBELLS
 Rubber Hex Dumbbells
Rubber Hex Dumbbells
 Cast Iron Adjustable Dumbbells
Cast Iron Adjustable Dumbbells
 Round Head Dumbbells
Round Head Dumbbells
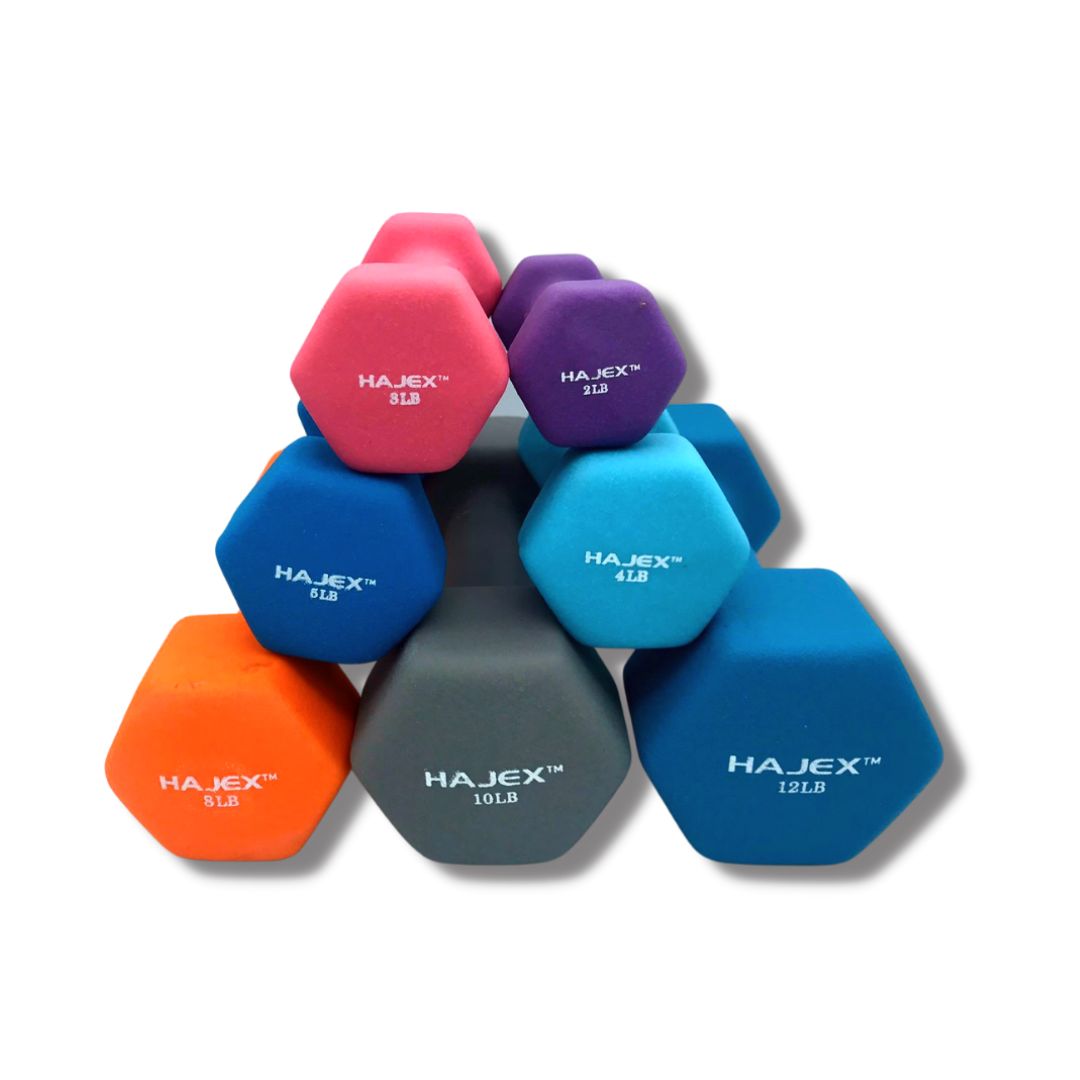 Neoprene Dumbbells
Neoprene Dumbbells
 BENCHES
BENCHES
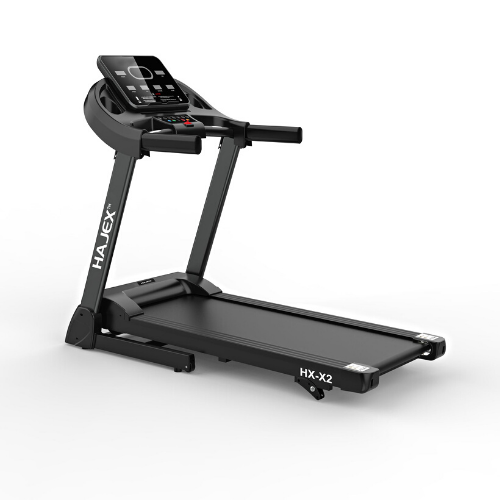 CARDIO
CARDIO
 BARBELL BARS
BARBELL BARS
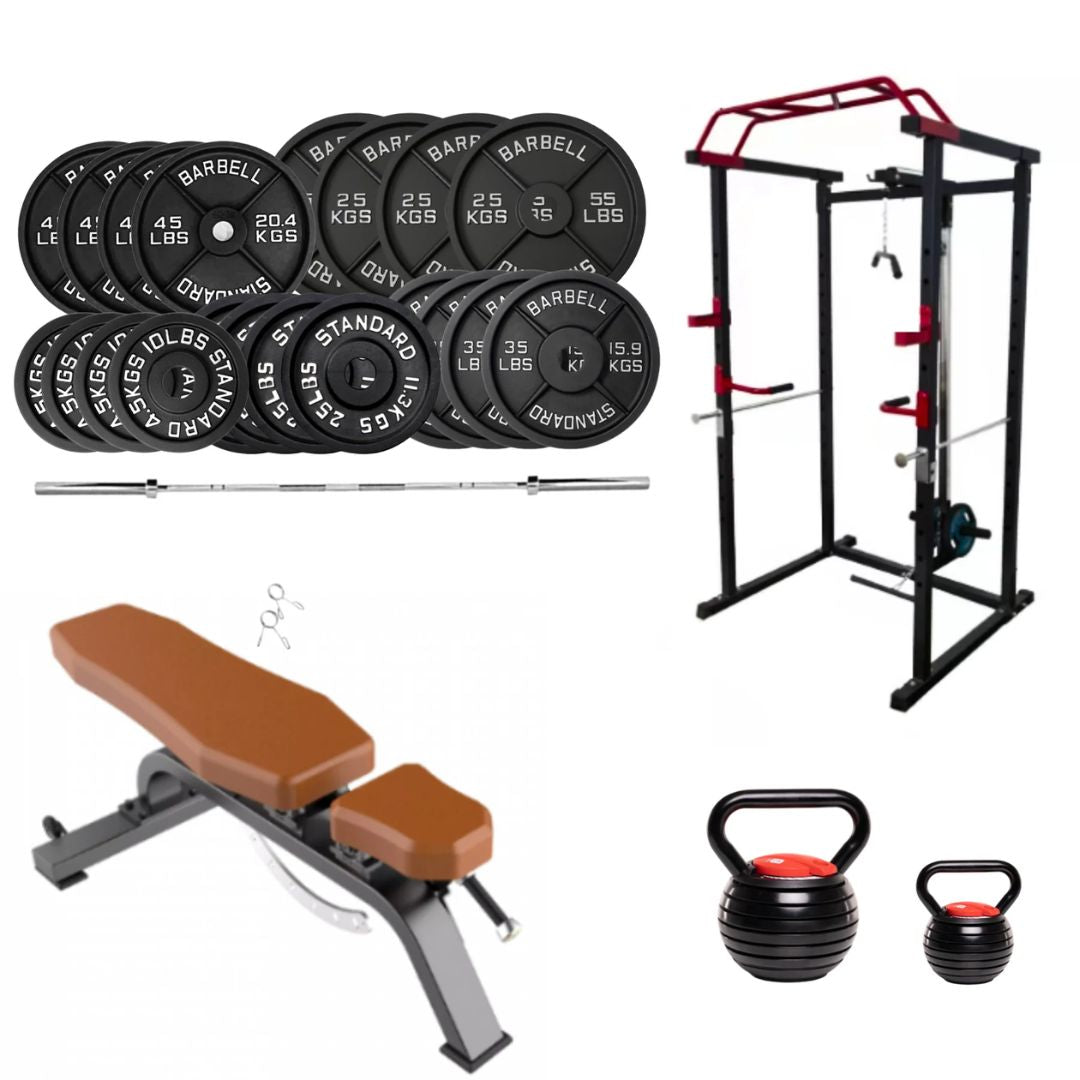 Home Gym Deals
Home Gym Deals
 Olympic Bumper Plates
Olympic Bumper Plates
 Tri Grip Plates
Tri Grip Plates
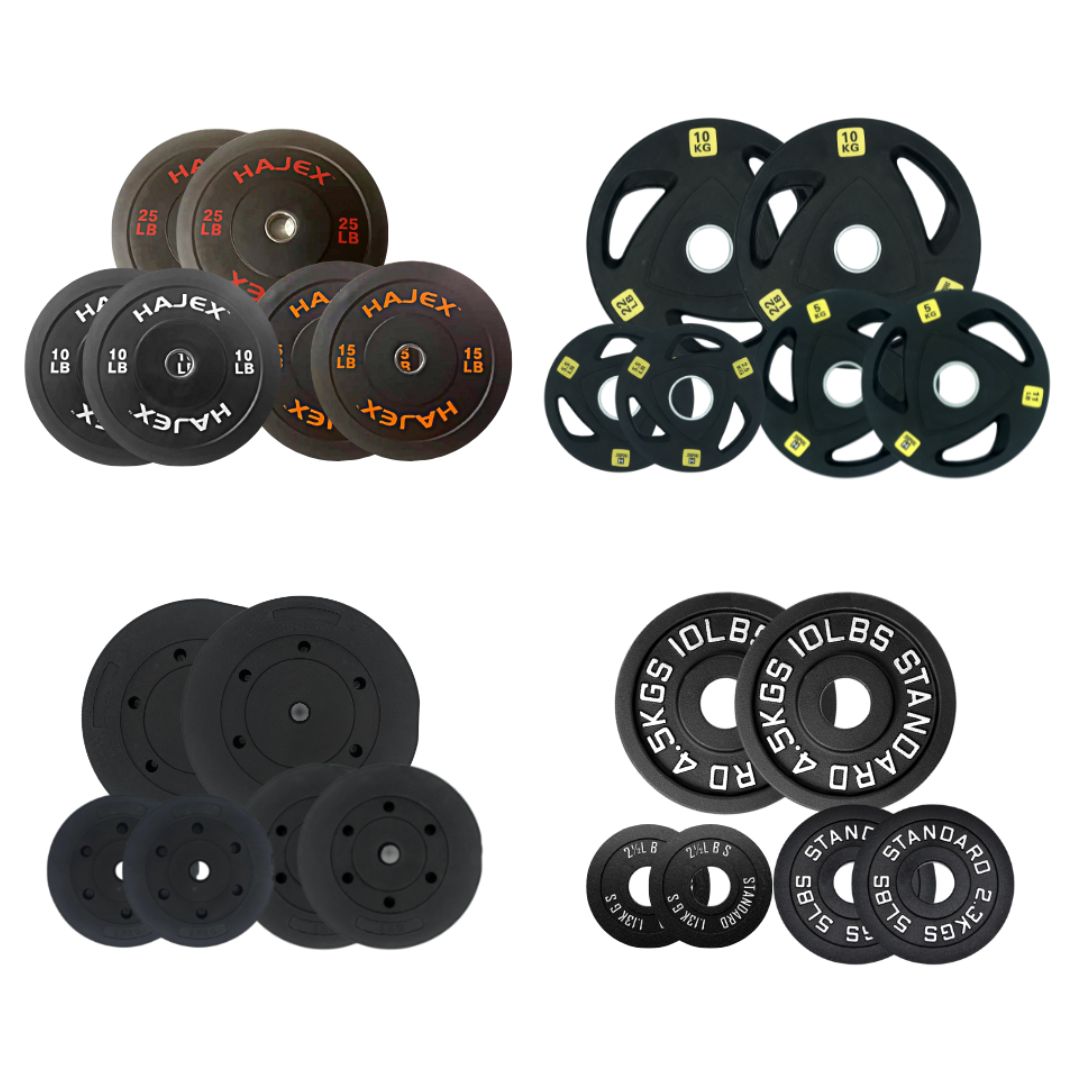 Weight Plates Combo
Weight Plates Combo
 Olympic Steel Hub Bumper Plates
Olympic Steel Hub Bumper Plates
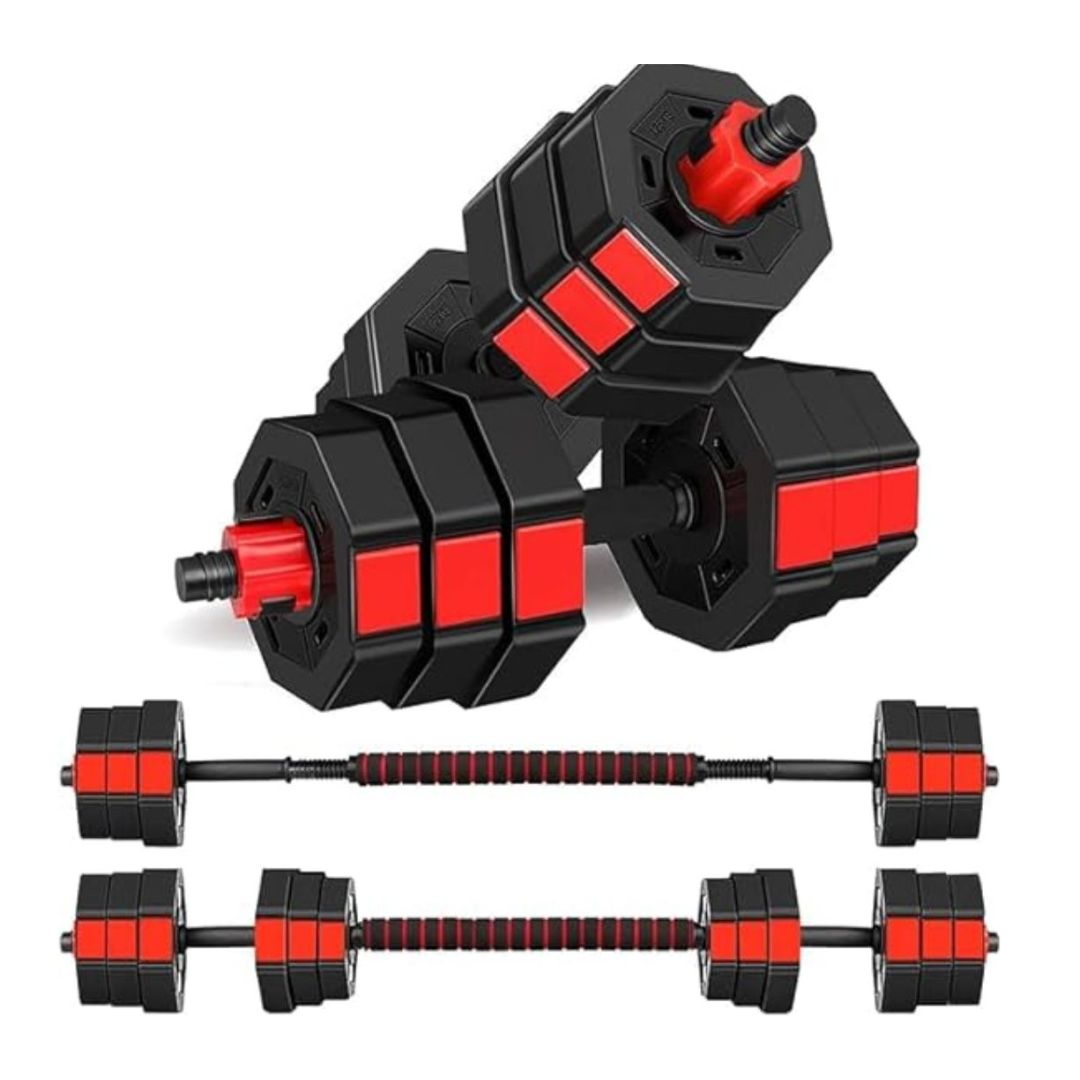 PVC Dumbbells
PVC Dumbbells
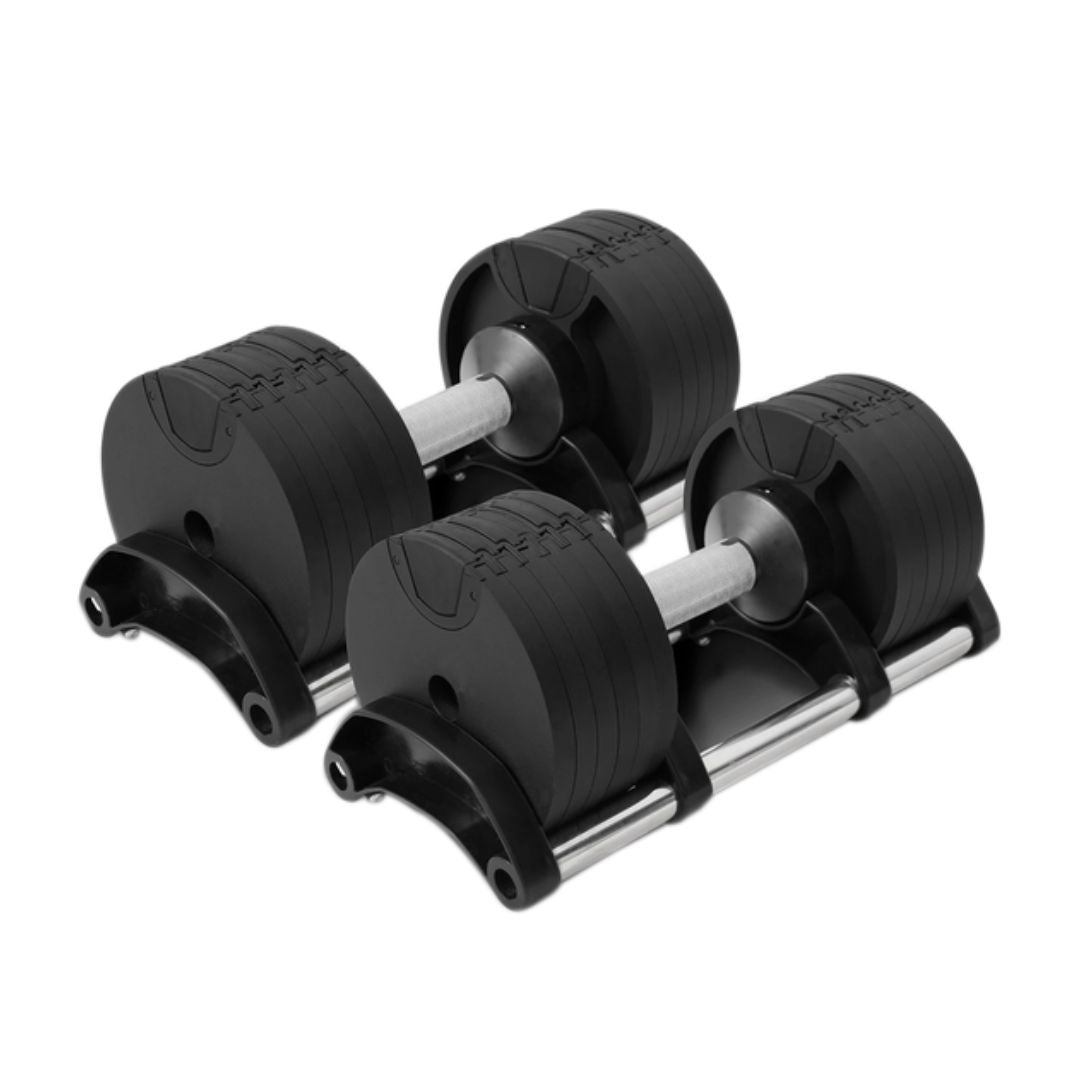 NUO Style Adjustable Dumbbells
NUO Style Adjustable Dumbbells
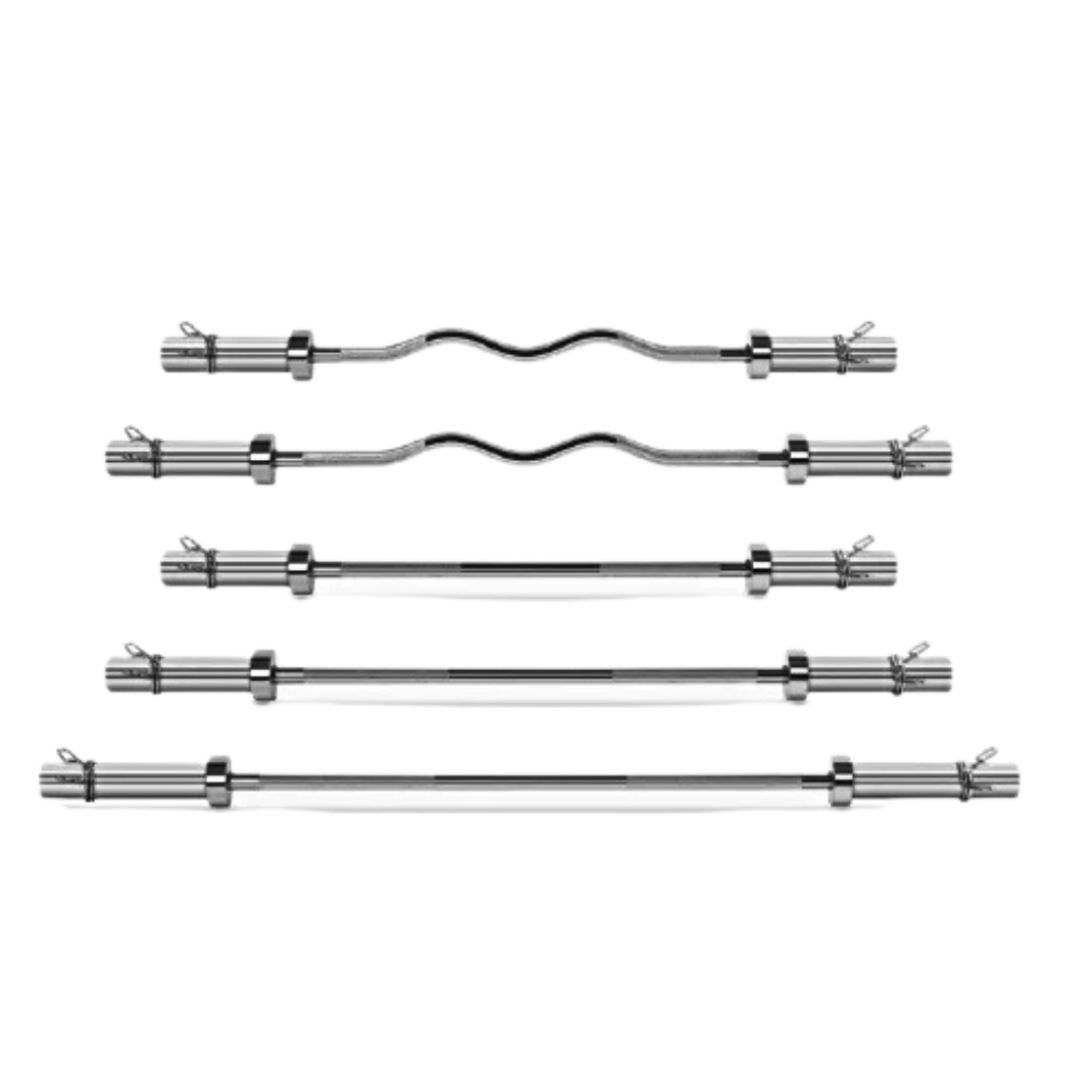 Olympic Barbells 2"
Olympic Barbells 2"
 Standard Barbells 1"
Standard Barbells 1"
 Fixed Weight Bars
Fixed Weight Bars
 Benches with Pulley & Rack
Benches with Pulley & Rack
 CARDIO
CARDIO
 Foldable Walking Pads
Foldable Walking Pads
 Exercise Bikes
Exercise Bikes
 RACKS, CAGES & SMITHS
RACKS, CAGES & SMITHS
 Smith Machines
Smith Machines
 Power Racks
Power Racks
 Squat Racks
Squat Racks
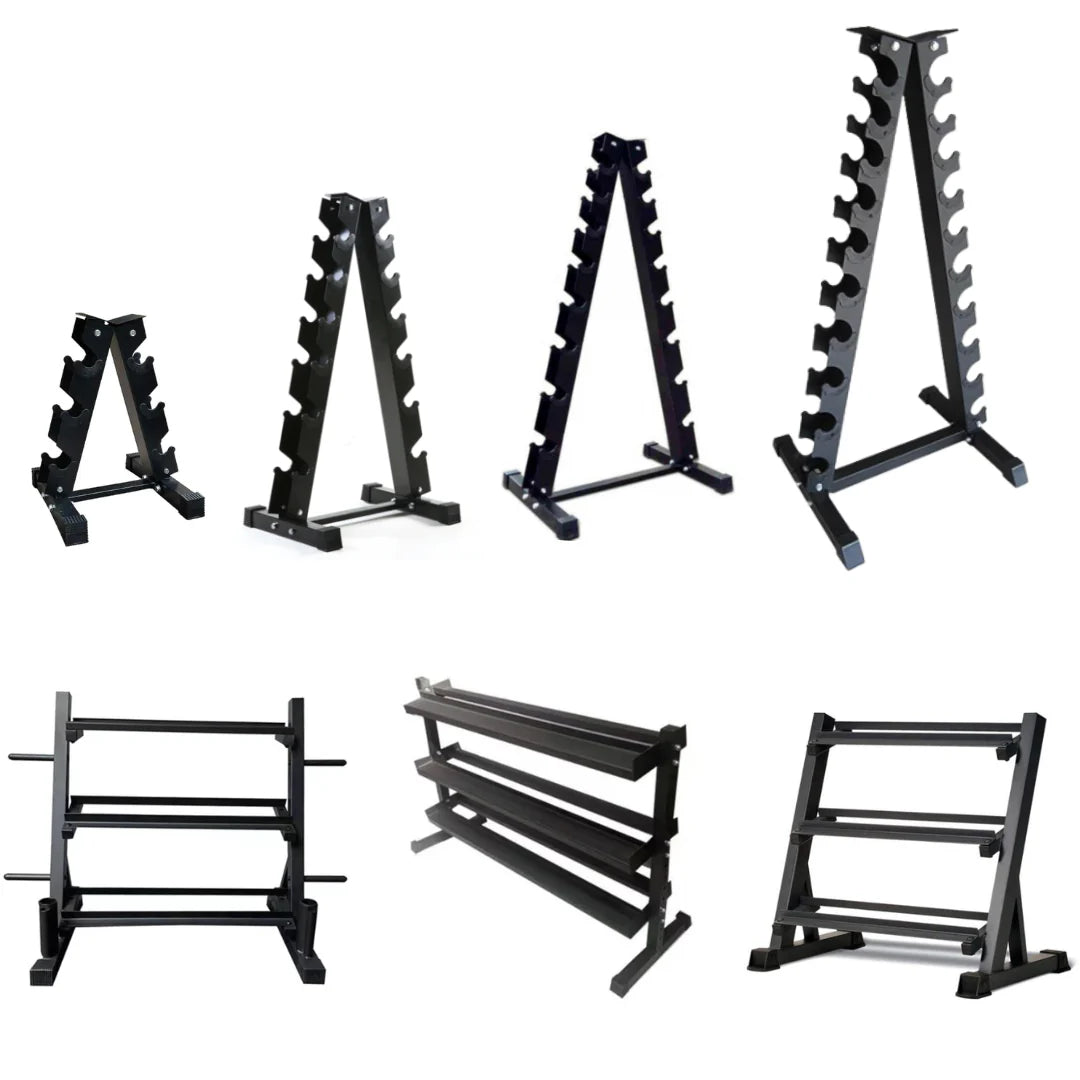 STORAGE RACKS
STORAGE RACKS
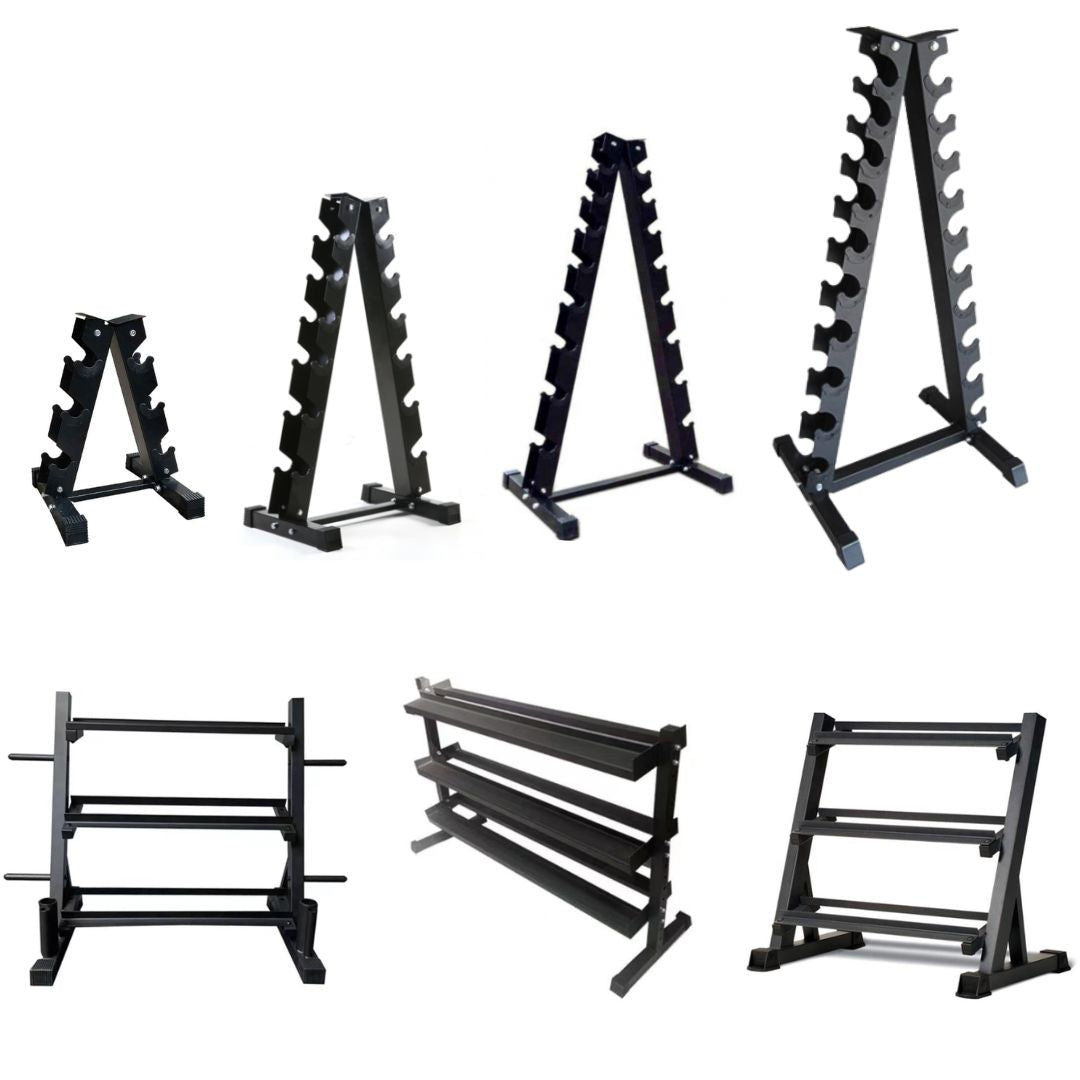 Dumbbell & Kettlebell Racks
Dumbbell & Kettlebell Racks
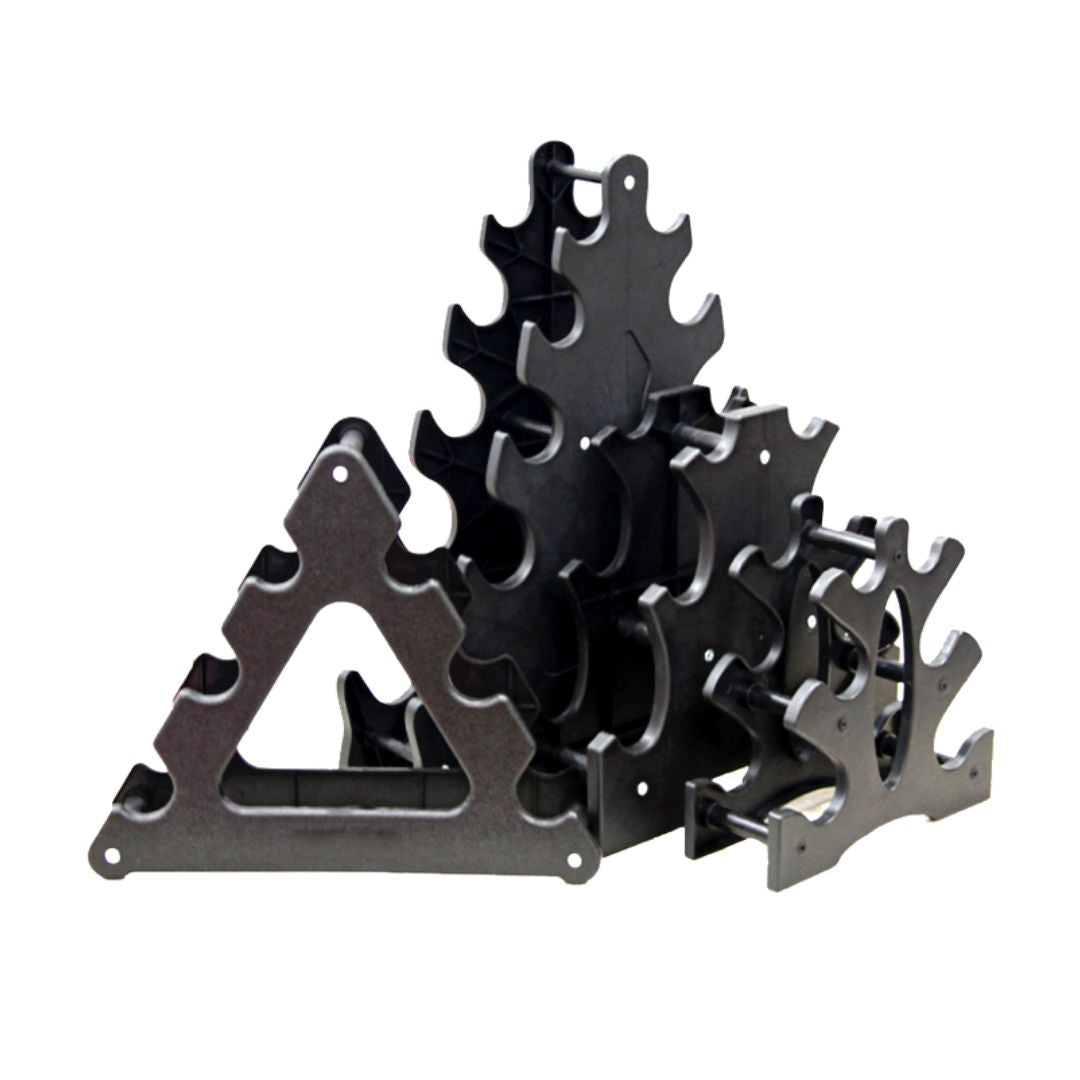 Mini Dumbbell Racks
Mini Dumbbell Racks
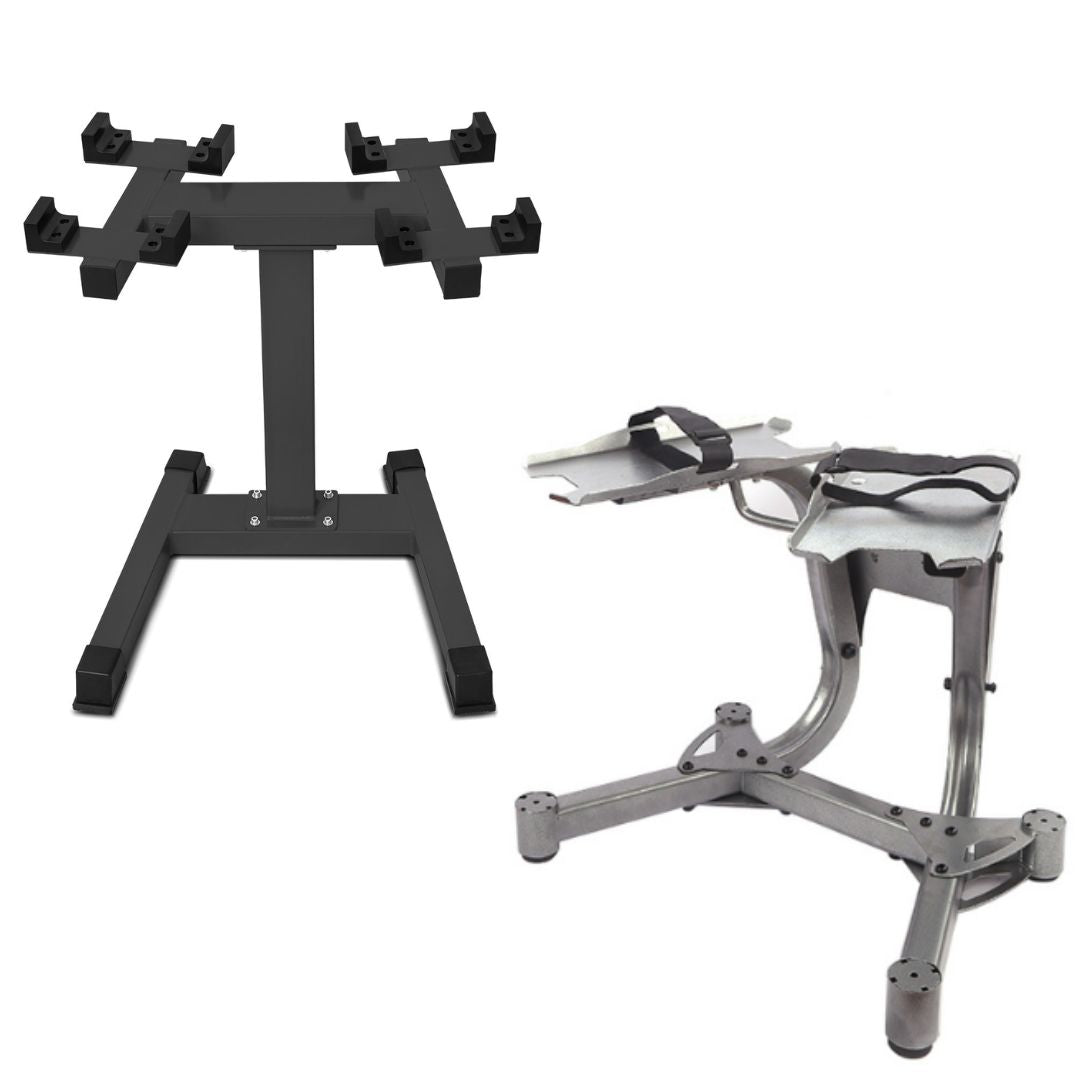 Adjusatble Dumbbell Stands
Adjusatble Dumbbell Stands
 MORE
MORE
 Kettlebells
Kettlebells
 Adjustable Kettlebells - Single & Pair
Adjustable Kettlebells - Single & Pair
 Floor Mats
Floor Mats
 Yoga
Yoga
 Push Up
Push Up
 Resistance Bands
Resistance Bands
 Barbell Pads
Barbell Pads
 Dumbbell Handles
Dumbbell Handles
 Jump Ropes
Jump Ropes